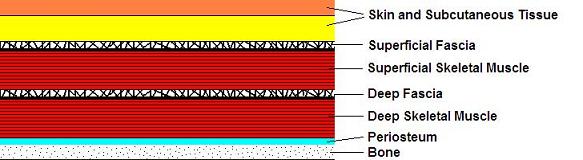
 1.The major characteristic of medical massage compared to any other type of body work is the selectivity of its application. There are four types of soft tissues that the massage practitioner deals with: skin with subcutaneous tissues, connective tissue structures, skeletal muscles and periosteum. Each type of soft tissue has its own unique structure and unique combination of peripheral receptors.
1.The major characteristic of medical massage compared to any other type of body work is the selectivity of its application. There are four types of soft tissues that the massage practitioner deals with: skin with subcutaneous tissues, connective tissue structures, skeletal muscles and periosteum. Each type of soft tissue has its own unique structure and unique combination of peripheral receptors.
Thus, methods of medical massage were designed selectively for each type of tissue separately and for each separate condition. Therefore, medical massage very precisely targets soft tissues on each level. The technical application of Medial Massage demands a layer-by-layer approach using special methods or techniques that have been developed for each type of soft tissue. To address the skin, the practitioner may use superficial effleurage, superficial friction, kneading of the fold of skin, and connective tissue massage. The best techniques to address superficial fascia are connective tissue massage and myofascial release. The superficial and deep muscular groups should be treated with trigger point therapy, postisometric muscular relaxation and myofascial release. To address the deep fascia, the practitioner may use connective tissue massage as well as kneading of the superficial muscular group applied in the inhibitory regime. The best way to address the periosteum is through the application of periostal massage and Cyriax's friction
2. Each method of medical massage has its own goals, techniques and level of application. However, the practitioner needs something which will hold together the application of the different methods of medical massage and unite them into one perfectly organized medical massage session. Therapeutic massage fulfills this goal. Therapeutic massage is used every time when the practitioner changes or applies a new method or technique of medical massage during the same session.
3. Medical massage is restricted to the parts of the body related to the pathological process. A full-body should never be used (except in case of Fibromyalgia) because the practitioner wants to concentrate on the soft tissues which show local or/and reflex abnormalities. The goal of such a selective approach is to work with correct combination of medical massage techniques and methods to activate peripheral receptors and elicit the correct response from the segment of the spinal cord which are responsible for the innervation of the affected area. Thus, the more precise the application of medical massage techniques, the better the results are.
4. Medical massage requires between 30 minutes and an hour session. However, the duration may fluctuate between 30 minutes and an one hour and a half.
5. After the first session, the patient has to have a break of 2-3 days to determine the initial reaction of the body to the therapy.
6. Medical massage therapy should be used as a course of treatment. Usually between 5 and 15 sessions should be required.The specific number of sessions depends upon the type of pathology and the age of the patient. When necessary, the course of treatment may be repeated after a break of 15-30 days, again depending upon the disorder and the age of the patient.
7. Each course of medical massage has to start with a diagnostic evaluation of the soft tissues. This allows the practitioner to select the optimal method of medical massage or the combination of massage procedures.
8. All pathological changes are recorded on prepared diagrams.
9. Each new session has to start with detailed questioning of the patient to clarify any changes which have occurred since the previous session or since the beginning of treatment. It allows the practitioner to evaluate the impact of medical massage on the patient.
10. Each session starts with massage of the paravertebral areas and the vertebral column in the level of segments of the spinal cord which innervate the affected inner organ or somatic structure.
11. In cases of disorders of the nervous and musculoskeletal systems, the greatest impact from medical massage is achieved by its application at the earliest sign of abnormality. Patients with a newly diagnosed inner organ disorder (e.g., Acute Gastritis) are less responsive to treatment compared to patients with the same, but chronic disorder(e.g., Chronic Gastritis). In cases of a newly diagnosed visceral disorder, the practitioner should work on the soft tissues in the areas where reflex zones may develop. In such cases, the practitioner uses the preventive role of massage therapy to extend periods of remission and to prevent further progress of abnormality. For these patients, regular application of therapeutic massage sessions is the first choice of treatment.
12. It is mandatory that a rest period of 5 to 10 minutes occurs after each medical massage session. The patient must either lie down or recline to decrease the possibility of autonomic reactions.
